Rochdale Town Hall on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rochdale Town Hall is a
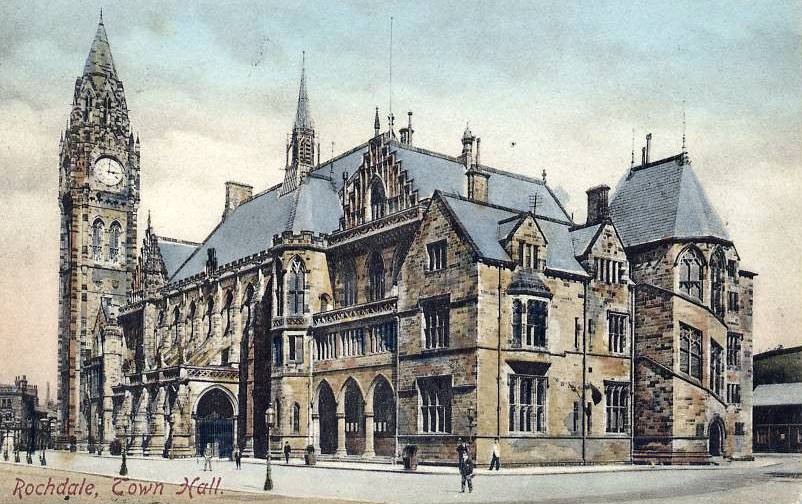 The frontage and principal entrance of the Town Hall face the
The frontage and principal entrance of the Town Hall face the 

 Murals in the former council chamber depict the inventions that drove the
Murals in the former council chamber depict the inventions that drove the
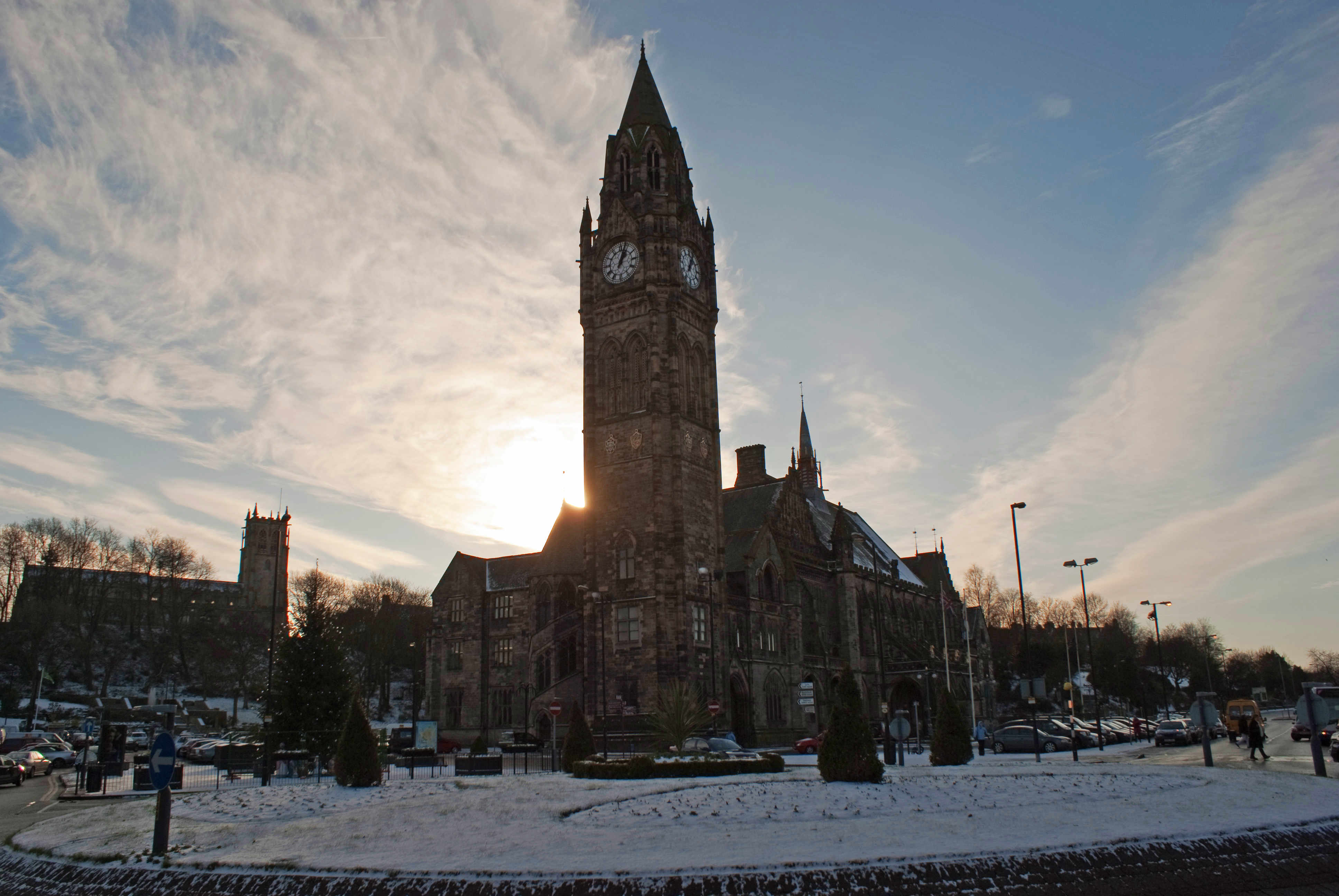 The Town Hall was
The Town Hall was
Victorian-era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardi ...
municipal building Municipal Building may refer to the following places:
United States Arkansas
*Crossett Municipal Building, Crossett, AR, List of RHPs in AR, listed on the NRHP in Arkansas
*Municipal Building (El Dorado, Arkansas), El Dorado, AR, List of RHPs in A ...
in Rochdale
Rochdale ( ) is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, at the foothills of the South Pennines in the dale on the River Roch, northwest of Oldham and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough ...
, Greater Manchester
Greater Manchester is a metropolitan county and combined authority, combined authority area in North West England, with a population of 2.8 million; comprising ten metropolitan boroughs: City of Manchester, Manchester, City of Salford, Salford ...
, England. It is "widely recognised as being one of the finest municipal buildings in the country",. and is recorded in the National Heritage List for England
The National Heritage List for England (NHLE) is England's official database of protected heritage assets. It includes details of all English listed buildings, scheduled monuments, register of historic parks and gardens, protected shipwrecks, an ...
as a designated Grade I listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
. The Town Hall functions as the ceremonial headquarters of Rochdale Metropolitan Borough Council
Rochdale Borough Council is the local authority of the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale in Greater Manchester, England. It is a metropolitan district council, one of ten in Greater Manchester and one of 36 in the metropolitan counties of England ...
and houses local government departments, including the borough's civil registration office.
Built in the Gothic Revival style
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
at a cost of £160,000 (£ in ), it was inaugurated for the governance of the Municipal Borough of Rochdale on 27 September 1871. The architect, William Henry Crossland
William Henry Crossland (Yorkshire, 1835 – London, 14 November 1908), known professionally as W.H. Crossland, was a 19th-century English architect and a pupil of George Gilbert Scott. His architectural works included the design of three building ...
, was the winner of a competition held in 1864 to design a new Town Hall. It had a clock tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
topped by a wooden spire with a gilded statue of Saint George and the Dragon
In a legend, Saint Georgea soldier venerated in Christianitydefeats a dragon. The story goes that the dragon originally extorted tribute from villagers. When they ran out of livestock and trinkets for the dragon, they started giving up a human tr ...
, both of which were destroyed by fire on 10 April 1883, leaving the building without a spire for four years. A new stone clock tower and spire in the style of Manchester Town Hall
Manchester Town Hall is a Victorian, Neo-gothic municipal building in Manchester, England. It is the ceremonial headquarters of Manchester City Council and houses a number of local government departments. The building faces Albert Square to th ...
was designed by Alfred Waterhouse
Alfred Waterhouse (19 July 1830 – 22 August 1905) was an English architect, particularly associated with the Victorian Gothic Revival architecture, although he designed using other architectural styles as well. He is perhaps best known f ...
, and erected in 1887.
Architectural historian Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (1 ...
described the building as possessing a "rare picturesque beauty". Its stained-glass
Stained glass is coloured glass as a material or works created from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant religious buildings. Although tradition ...
windows are credited as "the finest modern examples of their kind". The building came to the attention of Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, who was said to have admired it so much that he wished to ship the building, brick-by-brick, to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
had the United Kingdom been defeated in the Second World War.
History
Rochdale had developed into an increasingly large, populous, and prosperous urbanmill town
A mill town, also known as factory town or mill village, is typically a settlement that developed around one or more mills or factories, usually cotton mills or factories producing textiles. Europe
Italy
* ''Crespi d'Adda'', UNESCO World Her ...
since the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. Its newly built rail and canal network, and numerous factories, resulted in the town being "remarkable for many wealthy merchants".. In January 1856 the electorate of the Rochdale constituency petitioned the Privy Council
A privy council is a body that advises the head of state of a state, typically, but not always, in the context of a monarchic government. The word "privy" means "private" or "secret"; thus, a privy council was originally a committee of the mon ...
for the grant of a charter of incorporation
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the rec ...
under the Municipal Corporations Act 1835
The Municipal Corporations Act 1835 (5 & 6 Will 4 c 76), sometimes known as the Municipal Reform Act, was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in the incorporated boroughs of England and Wales. The legisl ...
, to constitute the town as a municipal borough
Municipal boroughs were a type of local government district which existed in England and Wales between 1835 and 1974, in Northern Ireland from 1840 to 1973 and in the Republic of Ireland from 1840 to 2002. Broadly similar structures existed in S ...
. This would give it limited political autonomy via an elected town council, comprising a mayor, aldermen
An alderman is a member of a municipal assembly or council in many jurisdictions founded upon English law. The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council member chosen by the elected members them ...
, and councillor
A councillor is an elected representative for a local government council in some countries.
Canada
Due to the control that the provinces have over their municipal governments, terms that councillors serve vary from province to province. Unl ...
s, to oversee local affairs. The petition was successful and the charter was granted in September 1856. The newly formed Rochdale Corporation—the local authority
Local government is a generic term for the lowest tiers of public administration within a particular sovereign state. This particular usage of the word government refers specifically to a level of administration that is both geographically-loca ...
for the Municipal Borough of Rochdale—suggested plans to build a town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
in which to conduct its business in May 1858. The site of an abandoned 17th century house known as the Wood was proposed. Six months later, in April 1860, Rochdale Corporation arranged to buy the site on the outskirts of the town centre for £4,730 (£ in ). However, plans were shelved due to lengthy negotiations and increasing land prices. In January 1864 the scheme resumed with a new budget of £20,000 (£ in ).
The wood and surrounding area were cleared, but it is unknown what became of the dispossessed; there was no legal requirement for the authorities to rehouse the former inhabitants.. A design competition to find a "neat and elegant building" was held by the Rochdale Corporation,. who offered the winning architect a prize of £100 (£ in ), and a Maltese cross
The Maltese cross is a cross symbol, consisting of four " V" or arrowhead shaped concave quadrilaterals converging at a central vertex at right angles, two tips pointing outward symmetrically.
It is a heraldic cross variant which developed f ...
souvenir. From the 27 entries received, William Henry Crossland
William Henry Crossland (Yorkshire, 1835 – London, 14 November 1908), known professionally as W.H. Crossland, was a 19th-century English architect and a pupil of George Gilbert Scott. His architectural works included the design of three building ...
's was chosen. The Rochdale-born Radical
Radical may refer to:
Politics and ideology Politics
*Radical politics, the political intent of fundamental societal change
*Radicalism (historical), the Radical Movement that began in late 18th century Britain and spread to continental Europe and ...
and Liberal
Liberal or liberalism may refer to:
Politics
* a supporter of liberalism
** Liberalism by country
* an adherent of a Liberal Party
* Liberalism (international relations)
* Sexually liberal feminism
* Social liberalism
Arts, entertainment and m ...
statesman John Bright
John Bright (16 November 1811 – 27 March 1889) was a British Radical and Liberal statesman, one of the greatest orators of his generation and a promoter of free trade policies.
A Quaker, Bright is most famous for battling the Corn Laws ...
laid the foundation stone on 31 March 1866. Construction was complete by 1871 although the cost had, by then, increased beyond expectations from the projected £40,000 to £160,000 (£ in ).
The Town Hall was one of several built in the textile towns of North West England
North West England is one of nine official regions of England and consists of the ceremonial counties of England, administrative counties of Cheshire, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire and Merseyside. The North West had a population of ...
following the Municipal Corporations Act 1835, but is one of only two in Greater Manchester built in the Gothic style. Between the setting of the foundation stone and the building's completion, revisions and additions were made to the original design. Money was "lavished" upon the decor and inventory, and the extra expenditure did not escape the ire of its critics. The cost of the building increased year-on-year through a combination of mismanagement, overspending and "unauthorised work". Public criticism of the high cost was aimed at Crossland and the Mayor of Rochdale, George Leach Ashworth, who oversaw the work. Nevertheless, Rochdale Town Hall was ultimately celebrated as "a source of pride", and its completion prompted celebration and rejoicing; it transformed a "derelict and marshy riverbank in to a huge romantic Gothic plaza". The opening ceremony on 27 September 1871 was performed by Mayor Ashworth, who had been instrumental in the changes made to the building's design.
In 1882 or 1883 dry rot
Dry rot is wood decay caused by one of several species of fungi that digest parts of the wood which give the wood strength and stiffness. It was previously used to describe any decay of cured wood in ships and buildings by a fungus which resul ...
was found in the high spire. On the recommendation of Rochdale's Borough Surveyor, contractors were engaged to rebuild it. The spire was to be demolished to clear the way for a replacement. It was rumoured that the workmen who were dismantling the top section of the wooden spire may have tried to speed up the dismantling process with matches and, at 9:20 am on 10 April 1883, a blaze was discovered. Despite the efforts of volunteers and the local fire brigade, 100 minutes after the discovery of the fire the entire spire, including a statue of Saint George and the Dragon
In a legend, Saint Georgea soldier venerated in Christianitydefeats a dragon. The story goes that the dragon originally extorted tribute from villagers. When they ran out of livestock and trinkets for the dragon, they started giving up a human tr ...
, had been destroyed. The cause of the fire was never established, but Rochdale's fire service was criticised for taking longer to respond to the blaze than Oldham
Oldham is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, amid the Pennines and between the rivers Irk and Medlock, southeast of Rochdale and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, wh ...
's (based south), despite the Rochdale Fire Brigade being based in the Town Hall. Alfred Waterhouse
Alfred Waterhouse (19 July 1830 – 22 August 1905) was an English architect, particularly associated with the Victorian Gothic Revival architecture, although he designed using other architectural styles as well. He is perhaps best known f ...
was given the task of designing a stone replacement. His work on the clock tower, which was built between 1885 and 1887 about further to the east than the original, shows many similarities to Manchester Town Hall
Manchester Town Hall is a Victorian, Neo-gothic municipal building in Manchester, England. It is the ceremonial headquarters of Manchester City Council and houses a number of local government departments. The building faces Albert Square to th ...
, which he also designed. The tower was opened in 1887; an inscribed plaque commemorates the fire of 1883.
On 15 January 1931, at the height of the Great Depression in the United Kingdom
The Great Depression in the United Kingdom also known as the Great Slump, was a period of national economic downturn in the 1930s, which had its origins in the global Great Depression. It was Britain's largest and most profound economic depress ...
, the Territorial Army was called to guard the Town Hall during a protest against unemployment and hunger.
In May 1938, Rochdale-born actress, singer and comedian Gracie Fields
Dame Gracie Fields (born Grace Stansfield; 9 January 189827 September 1979) was an English actress, singer, comedian and star of cinema and music hall who was one of the top ten film stars in Britain during the 1930s and was considered the h ...
was granted Honorary Freedom of the Borough for her contribution to entertainment. "When the ceremony was over, Gracie went onto the town hall balcony to receive the cheers and good wishes of the thousands of people who were packing the streets below."
Although it is not fully understood how it came to his attention, Rochdale Town Hall was admired by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
. It has been suggested a visit by Hitler in 1912–13 while staying with his half-brother Alois Hitler Jr. in Liverpool
Liverpool is a city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the 10th largest English district by population and its metropolitan area is the fifth largest in the United Kingdom, with a popul ...
, or military intelligence on Rochdale, or information from Nazi sympathiser William Joyce
William Brooke Joyce (24 April 1906 – 3 January 1946), nicknamed Lord Haw-Haw, was an American-born fascist and Nazi propaganda broadcaster during the Second World War. After moving from New York to Ireland and subsequently to England, J ...
(who had lived in Oldham
Oldham is a large town in Greater Manchester, England, amid the Pennines and between the rivers Irk and Medlock, southeast of Rochdale and northeast of Manchester. It is the administrative centre of the Metropolitan Borough of Oldham, wh ...
), brought the building to his attention. Hitler admired the architecture so much that it is believed he wished to ship the building, brick-by-brick, to Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
had German-occupied Europe
German-occupied Europe refers to the sovereign countries of Europe which were wholly or partly occupied and civil-occupied (including puppet governments) by the military forces and the government of Nazi Germany at various times between 1939 an ...
encompassed the United Kingdom. Rochdale was broadly avoided by German bombers during the Second World War.
Features
Location
At OS Grid Reference (53.6156°, −2.1594°), Rochdale Town Hall is the centerpiece of Rochdale, located in Town Hall Square to the south of The Esplanade and theRiver Roch
The River Roch is a river in Greater Manchester in North West England, a tributary of the River Irwell.
Course
Rising on Chelburn Moor (south of Todmorden in the Pennines), the river flows south through Littleborough towards Rochdale where ...
. The Parish Church of St Chad is situated by the wooded hillside behind the Town Hall.. In Town Hall Square, opposite the Town Hall, is a statue of John Bright
John Bright (16 November 1811 – 27 March 1889) was a British Radical and Liberal statesman, one of the greatest orators of his generation and a promoter of free trade policies.
A Quaker, Bright is most famous for battling the Corn Laws ...
, dated 1891, and the Rochdale War Memorial. Bright was a Rochdale-born orator, pacifist and Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members of ...
for Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West ...
known for his campaigns to repeal the Corn Laws
The Corn Laws were tariffs and other trade restrictions on imported food and corn enforced in the United Kingdom between 1815 and 1846. The word ''corn'' in British English denotes all cereal grains, including wheat, oats and barley. They were ...
as well as his opposition to slavery in the United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Sl ...
and the Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
. Touchstones Rochdale art gallery and local studies centre is across The Esplanade.
Exterior and layout
 The frontage and principal entrance of the Town Hall face the
The frontage and principal entrance of the Town Hall face the River Roch
The River Roch is a river in Greater Manchester in North West England, a tributary of the River Irwell.
Course
Rising on Chelburn Moor (south of Todmorden in the Pennines), the river flows south through Littleborough towards Rochdale where ...
, and comprises a portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
of three arches intersected by buttresses. Decorating the main entrance are stone crocket
A crocket (or croquet) is a small, independent decorative element common in Gothic architecture. The name derives from the diminutive of the French ''croc'', meaning "hook", due to the resemblance of crockets to a bishop's crosier.
Description
...
s, gargoyle
In architecture, and specifically Gothic architecture, a gargoyle () is a carved or formed grotesque with a spout designed to convey water from a roof and away from the side of a building, thereby preventing it from running down masonry walls ...
s, and finials
A finial (from '' la, finis'', end) or hip-knob is an element marking the top or end of some object, often formed to be a decorative feature.
In architecture, it is a small decorative device, employed to emphasize the apex of a dome, spire, tower ...
. Four gilded lions above a parapet around three sides of the portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cult ...
bear shields carrying the coats of arms of Rochdale Council and the hundred of Salford
The Salford Hundred (also known as Salfordshire) was one of the subdivisions of the historic county of Lancashire, in Northern England (see:Hundred (county division). Its name alludes to its judicial centre being the township of Salford (the s ...
.
Rochdale Town Hall is wide, deep, and is faced with millstone grit quarried from Blackstone Edge
Blackstone Edge ( ) is a gritstone escarpment at 472 m (1,549 feet) above sea level in the Pennine hills surrounded by moorland on the boundary between Greater Manchester and West Yorkshire in England.
History
Crossing the escarpment is Bl ...
and Todmorden
Todmorden ( ; ) is a market town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in the Upper Calder Valley in Calderdale, West Yorkshire, England. It is north-east of Manchester, south-east of Burnley and west of Halifax, West Yorkshire, Hal ...
. Although now blackened by industrial pollution, the building has been described as a "rich example of domestic Gothic architecture". Naturalistic carved foliage on the exterior recalls the style of Southwell Minster
Southwell Minster () is a minster and cathedral in Southwell, Nottinghamshire, England. It is situated miles from Newark-on-Trent and from Mansfield. It is the seat of the Bishop of Southwell and Nottingham and the Diocese of Southwell and N ...
, and the architecture is influenced by Perpendicular Period
Perpendicular Gothic (also Perpendicular, Rectilinear, or Third Pointed) architecture was the third and final style of English Gothic architecture developed in the Kingdom of England during the Late Middle Ages, typified by large windows, four-c ...
and medieval town halls of continental Europe. The building has been likened to Manchester Town Hall
Manchester Town Hall is a Victorian, Neo-gothic municipal building in Manchester, England. It is the ceremonial headquarters of Manchester City Council and houses a number of local government departments. The building faces Albert Square to th ...
, Manchester Assize Courts
The Manchester Assize Courts was a building housing law courts on Great Ducie Street in the Strangeways district of Manchester, England. It was tall and from 1864 to 1877 the tallest building in Manchester. Widely admired, it has been referred to ...
, the Royal Courts of Justice
The Royal Courts of Justice, commonly called the Law Courts, is a court building in Westminster which houses the High Court and Court of Appeal of England and Wales. The High Court also sits on circuit and in other major cities. Designed by Ge ...
, and St Pancras railway station
St Pancras railway station (), also known as London St Pancras or St Pancras International and officially since 2007 as London St Pancras International, is a central London railway terminus on Euston Road in the London Borough of Camden. It is ...
, all products of the Gothic Revival architectural movement. The stained glass windows, some of which were designed by William Morris
William Morris (24 March 1834 – 3 October 1896) was a British textile designer, poet, artist, novelist, architectural conservationist, printer, translator and socialist activist associated with the British Arts and Crafts Movement. He ...
, have been described as "the finest modern examples of their kind". At each end of the frontage is an octagonal staircase.
In the words of Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (1 ...
, Rochdale Town Hall has "a splendidly craggy exterior of blackened stone". The building has a roughly symmetrical E-shaped plan, and is broken down into three self-contained segments: a central Great Hall and transverse wings at each end, which have variously been used as debating chambers, corporation-rooms, trade and a public hall. The south-east wing used to house the magistrates' court
A magistrates' court is a lower court where, in several jurisdictions, all criminal proceedings start. Also some civil matters may be dealt with here, such as family proceedings.
Courts
* Magistrates' court (England and Wales)
* Magistrate's Cour ...
s, and the north-west wing the mayor's rooms. In the north-east is a tower. Access to the main entrance is through a central porte cochere
Porte may refer to:
*Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
*Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
*John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
*Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who competes ...
. The façade extends across 14 bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a narr ...
, of which the Great Hall accounts for seven. On both sides, the outermost bays rise to three storeys. They flank asymmetric round-headed arcades—two to the left and three to the right, all of single-storey height—which sit below plain mullion
A mullion is a vertical element that forms a division between units of a window or screen, or is used decoratively. It is also often used as a division between double doors. When dividing adjacent window units its primary purpose is a rigid supp ...
ed windows, balconies and ornately decorated gable
A gable is the generally triangular portion of a wall between the edges of intersecting roof pitches. The shape of the gable and how it is detailed depends on the structural system used, which reflects climate, material availability, and aesth ...
s.

Clock tower
The presentclock tower
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
, which has a stone spire, was built to replace the one destroyed in the 1883 fire. It was designed by Alfred Waterhouse
Alfred Waterhouse (19 July 1830 – 22 August 1905) was an English architect, particularly associated with the Victorian Gothic Revival architecture, although he designed using other architectural styles as well. He is perhaps best known f ...
in a similar style to one of his earlier works, the clock tower of Manchester Town Hall
Manchester Town Hall is a Victorian, Neo-gothic municipal building in Manchester, England. It is the ceremonial headquarters of Manchester City Council and houses a number of local government departments. The building faces Albert Square to th ...
. The first stone was laid by Thomas Schofield JP, Alderman
An alderman is a member of a Municipal government, municipal assembly or council in many Jurisdiction, jurisdictions founded upon English law. The term may be titular, denoting a high-ranking member of a borough or county council, a council membe ...
and Rochdale Borough Councillor
A councillor is an elected representative for a local government council in some countries.
Canada
Due to the control that the provinces have over their municipal governments, terms that councillors serve vary from province to province. Unl ...
, on 19 October 1885 and the tower was declared complete on 20 June 1887, the Golden Jubilee
A golden jubilee marks a 50th anniversary. It variously is applied to people, events, and nations.
Bangladesh
In Bangladesh, golden jubilee refers the 50th anniversary year of the separation from Pakistan and is called in Bengali ''"সু ...
of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
. It contains five bells which ring on the hour and at 15-minute intervals. The design of the original tower was more elaborate and higher than its successor, which is tall.
The tower rises from a plinth
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In c ...
and has four stages including the gable-headed clock stage, which is also decorated with pinnacles. A small stone spire completes the composition.
Interior

 Murals in the former council chamber depict the inventions that drove the
Murals in the former council chamber depict the inventions that drove the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
, and the Great Hall is adorned with a large fresco of the signing of Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
by artist Henry Holiday
Henry Holiday (17 June 183915 April 1927) was a British historical genre and landscape painter, stained-glass designer, illustrator, and sculptor. He is part of the Pre-Raphaelite school of art.
Life Early years and training
Holiday was born ...
, although the painting is dirty. Responsibility for the decoration of the interior was given to Heaton, Butler and Bayne
Heaton, Butler and Bayne were an English firm who produced stained-glass windows from 1862 to 1953.
History
Clement Heaton (1824–82) Fleming, John & Hugh Honour. (1977) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Decorative Arts. '' London: Allen Lane, p. 371. ...
, who incorporated floor tiles that were manufactured by Mintons
Mintons was a major company in Staffordshire pottery, "Europe's leading ceramic factory during the Victorian era", an independent business from 1793 to 1968. It was a leader in ceramic design, working in a number of different ceramic bodies, ...
and decorated with the local insignia and the Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varian ...
.. The stone Grand Staircase, which leads from the vestibule to the Great Hall, is decorated with stained glass; such glass windows decorate most of the Town Hall and are considered to be the finest example of the work of Heaton, Butler and Bayne. The medieval style Great Hall, described by Pevsner as a room of "great splendour and simplicity", has a hammerbeam roof
A hammerbeam roof is a decorative, open timber roof truss typical of English Gothic architecture and has been called "...the most spectacular endeavour of the English Medieval carpenter". They are traditionally timber framed, using short beams pr ...
flanked by statues of angels, in a design that resembles Westminster Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
.
James Jepson Binns
James Jepson Binns (c. 1855–11 March 1928) was a pipe organ builder based in Leeds, West Yorkshire, England.
Organs
Pipe organs at the following locations were either built or rebuilt by James Jepson Binns or his JJ Binns company. A number of ...
built the town hall's pipe organ in 1913; it was rebuilt in 1979 by J.W. Walker & Sons Ltd.
Heritage status and function
 The Town Hall was
The Town Hall was listed
Listed may refer to:
* Listed, Bornholm, a fishing village on the Danish island of Bornholm
* Listed (MMM program), a television show on MuchMoreMusic
* Endangered species in biology
* Listed building, in architecture, designation of a historicall ...
at Grade I on 25 October 1951. Such buildings are defined as being of "exceptional interest, sometimes considered to be internationally important". In February 2001, it was one of 39 Grade I listed buildings
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
, and 3,701 listed buildings of all grades, in Greater Manchester. Within the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale
The Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale is a metropolitan borough of Greater Manchester in North West England. It is named after its largest town, Rochdale, The borough covers other outlying towns and villages with a population of 206,500 at the ...
, it is one of only three Grade I listed buildings, and 312 listed buildings of all grades.
Although the majority of local government functions now take place within Number One Riverside
Number One Riverside is a multi-use public building in Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England. It incorporates Rochdale Metropolitan Borough Council civic offices and customer service centre, Rochdale Central Library as well as conference faciliti ...
, Rochdale Town Hall continues to be used for cultural and ceremonial functions. For instance, it is used for the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale's mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
alty, civil registry
Civil registration is the system by which a government records the vital events (births, marriages, and deaths) of its citizens and residents. The resulting repository or database has different names in different countries and even in differen ...
, and for formal naturalisation in British Citizenship ceremonies.
See also
*Grade I listed buildings in Greater Manchester
There are 48 Grade I listed buildings in Greater Manchester, England. In the United Kingdom, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of special architectural, historical or cultural sign ...
*Listed buildings in Rochdale
Rochdale is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Rochdale, Greater Manchester, England, and it is unparished. The town and the surrounding countryside contain 139 listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for England. O ...
References
Footnotes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * *External links
{{Good article Grade I listed buildings in Greater Manchester Alfred Waterhouse buildings Government buildings completed in 1871 Buildings and structures in Rochdale Gothic Revival architecture in Greater Manchester City and town halls in Greater Manchester William Henry Crossland buildings